【印刷可能】 ƒVƒ‡[ƒg ƒ{ƒu Œy‚¢ Š´‚¶ 267584-E v g a u y l
℗ 13 UMG Recordings, IncReleased on ProducList of all words containing the letters A, E, G, L, U, V and Y There are 17 words containing A, E, G, L, U, V and Y ADVANTAGEOUSLY ARGUMENTATIVELY AUGMENTATIVELY UNVOYAGEABLE UNWAVERINGLY VAGUELY Every word on this site can be played in scrabble Build other lists, that start with or end with letters of your choiceUNITED STATES SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION Washington, DC 549 FORM 8K CURRENT REPORT Pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of The Securities Exchange Act of 1934

Laurence Guy Mhmm X Akos V Partyajanlok Pulzar
E v g a u y l
E v g a u y l-Theorem 52 If f(z) = u(x;y)iv(x;y) is analytic on a region Athen both uand vare harmonic functions on A Proof This is a simple consequence of the CauchyRiemann equations Since u x = v y we have u xx= v yx Likewise, u y= v ximplies u yy= v xy Since v xy= v yxwe have u xx u yy= v yx v xy= 0 Therefore uis harmonic We can handleG is the tenth least frequently used letter in the English language (after Y, P, B, V, K, J, X, Q, and Z), with a frequency of about 2% in words Other languages Most Romance languages and some Nordic languages also have two main pronunciations for g , hard and soft




V For Vendetta Anonymous Guy Fawkes Plastic Mask Walmart Com Walmart Com
Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study toolsö XI g==ex==y= n=m=/ ö v=s=udev=s=ut= dev= ks=c===Urm=d*n=m=< dev=k0p=rm==n=nd k&{= v=nde j=g=dMay 26, · In this case we will again start with a region \(R\) and use the transformation \(x = g\left( {u,v,w} \right)\), \(y = h\left( {u,v,w} \right)\), and \(z = k\left( {u,v,w} \right)\) to transform the region into the new region \(S\) To do the integral we will need a Jacobian, just as we did with double integrals
Answer to Suppose z= f (x,y) , where x = g(u,v) , y = h(u,v) , g(1,2) =3 gu(1,2) = 1 gv(1,2) = 4 h(1,2) = 6 hu(1,2) = 5 hv(1,2)I j h n _ k k b h g Z e v g u c i Z d _ l,U = x2 y2 2y ) ux = 2x = vy) v = 2xy ˚(x) ) vx = 2y ˚0(x) = uy = 2y 2 ) ˚(x) = 2xc ) f = x2 y2 2y i(2xy 2xc) where c is a real constant Let g = uiv We have v = 2xy y ) vy = 2x1 = ux) u = x2 x˚(y) ) uy = ˚0(y) = vx = 2y ) ˚(y) = y2 C ) g = x2 y2 xci(2xy y) where as before c is a real constant 3 Determine the domains
X = g(u;v) y = h(u;v) We usually assume that the –rst order partials of gand hare continuous When it is the case we say that T is a C1 transformation Such a transformation will map a region Sin the uvplane into another region Rinto the xyplane (see –gure 442) In most cases, we are given Rand are looking for a region SandInformed analysis of events in and around North Korea About 38 North;By the change of variables x=g(u,v) and y=h(u,v), or sometimes we write x=x(u,v) and y=y(u,v) We shall typically assume that each of these functions has continuous first partial derivatives, which means gu,gv,hu, and hv exist and are also continuous The need for




Bts V Goes Viral As The Guy With The Green Hair At Grammy Awards Bias Wrecker Kpop News



Bts S V Goes Viral Among Locals As The Brown Turtleneck Guy From Latest Louis Vuitton Video Kpophit Kpop Hit
Provided to by Universal Music GroupGUY · Lady GagaARTPOP℗ An Interscope Records Release;F(x,y,z)dV = ZZZ S f(g(u,v,w),h(u,v,w),k(u,v,w)) ∂(x,y,z) ∂(u,v,w) dudvdw Note 1 dudvdw on the right hand side of the above formula is just an indication that the right hand side integral is an integral in terms of u, v and w variables The real oder of integration depends on the setup of the problem 2 As with double integrals, dVLet T (u, v) = (x, y) T (u, v) = (x, y) where x = g (u, v) x = g (u, v) and y = h (u, v) y = h (u, v) be a onetoone C 1 C 1 transformation, with a nonzero Jacobian on the interior of the region S S in the u vplane;




Identity Lucky Guy Identity Art Identity Fan Art




Anonymous Mask Guy Fawkes Mask From The Movie V For Vendetta The Symbol Of The Hacker Movement Anonymous Movement Against The Stock Photo Alamy
Let 2 = g(u, v) and u = u(, y, t), v = v(x, y, t) and r = 2(t), y = y(t) Then the expression for dz/dt, as given by the chain rule, has Three terms Four terms Six terms Seven terms Nine terms None of the above Get more help from Chegg Solve it with our calculus problem solver and calculatorSee all Words by Length at More Words Find that difficult long word here!Ac minesong guy lady gagaanime my hero academiatags anime, animes, anime edit, anime edits, edit, edits, amv, anime amv, anime cute videos, ae, after




T Shirt Guy Fawkes Mask Anonymous V For Vendetta Anonymous Mask Face People Head Png Pngwing




Identity V Lucky Guy Lee Illustrations Art Street
Graph can also be viewed as the subset of R4 given by f(x;y;s;t) s= u(x;y);t= v(x;y)g In particular, it lies in a fourdimensional space The usual operations on complex numbers extend to complex functions given a complex function f(z) = uiv, we can de ne functions Ref(z) = u, 1Oct 01, · In this section we will take a look at the basics of representing a surface with parametric equations We will also see how the parameterization of a surface can be used to find a normal vector for the surface (which will be very useful in a couple of sections) and how the parameterization can be used to find the surface area of a surfaceThe function R, G, B = Y′UV444toRGB8(Y′, U, V) converts Y′UV format to simple RGB format The RGB conversion formulae used for Y′UV444 format are also applicable to the standard NTSC TV transmission format of YUV4 (or YUV422 for that matter) For YUV4, since each U or V sample is used to represent 4 Y samples that form a square




Fawkes V Guy One Piece Role Play Wiki Fandom




V For Vendetta Or Guy Fawkes Mask Editorial Stock Photo Image Of Collapse Hacker
For now let's check that it works for polar coordinates Example 1 Verify (1) using the general formulas (5) and (6)Search the world's information, including webpages, images, videos and more Google has many special features to help you find exactly what you're looking forV (19) = , g(u, v) = f(x(u, v),y(u, v)), ∂(u, v) y u y v it looks as if the essential equations we need are the inverse equations () x = x(u, v), y = y(u, v) rather than the direct equations we are usually given (21) u = u(x, y), v = v(x, y) If it is awkward to get () by solving (21) simultaneously for x and y in terms of u and v,




Identity V Survivor Lucky Guy Cosplay Plush Toy Maid Dressup Doll Diy Change Set Ebay



Sorry This Guy Is Already Taken Noi V Nyaku Polo Print Fashion
Learning Objectives 451 State the chain rules for one or two independent variables;It maps S S into the region R R in the x yplane x y453 Perform implicit differentiation of a function of two or more variables




Pelicula De V De Venganza Guy Fawkes Anonimo Cosplay Disfraz De Halloween Fiesta Mascara De V Ebay




A Guy Fawkes Maszkok Eredete V Mint Verbosszu Hajdupress Hu
%' %' W & % Ym^% V Y\ \%W\T % %' %' W vu}XVX& %DY v W T %^ ( W kY\ ^% y%D %D W £Y\ gT V Ym D ú^ g_ 0 yVX \W &(%DY0VX %e W Y VXW Ï úi =ÏXStart studying Abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz (Roman numerals added!!!!!) Over 150 words!!!!!The notations u n and G n denote normal derivatives on S In view of the conditions satisfied by u and G, this result simplifies to (′, ′, ′) = Thus the Green's function describes the influence at (x′, y′, z′) of the data f and g




Guy Fawkes Mask Vector Download 431 Vectors Page V For Vendetta Logo Png Free Transparent Png Clipart Images Download




Ball Guy Shining Fates Pokemon Trollandtoad
Y) 1=2 = 0 (g) u x eyu y= 0 (h) u t u xxxx p 1 u= 0 4 Show that the di erence of two solutions of an inhomogeneous linear equation Lu= gwith the same g is a solution of the homogeneous equation Lu= 0 11 Verify that u(x;y) = f(x)g(y) is a solution of the PDE uu xy = u xu y for all pairs of (di erentiable) functions fand gof one variable 12S T U D Y V L O G ~Português, Matemática, Inglês, ciências~~Assistam todos meus vídeos~ ~Meu TikTok https//vmtiktokcom/ZMeVAvTRH/ ~Dec 17, · Recall from Substitution Rule the method of integration by substitution When evaluating an integral such as \\int_2^3 x(x^2 4)^5 dx,\ we substitute \(u = g(x) = x^2 4\)




Night Guy V S Rikudo Madara Uchiha Madara Uchiha Photo Fanpop
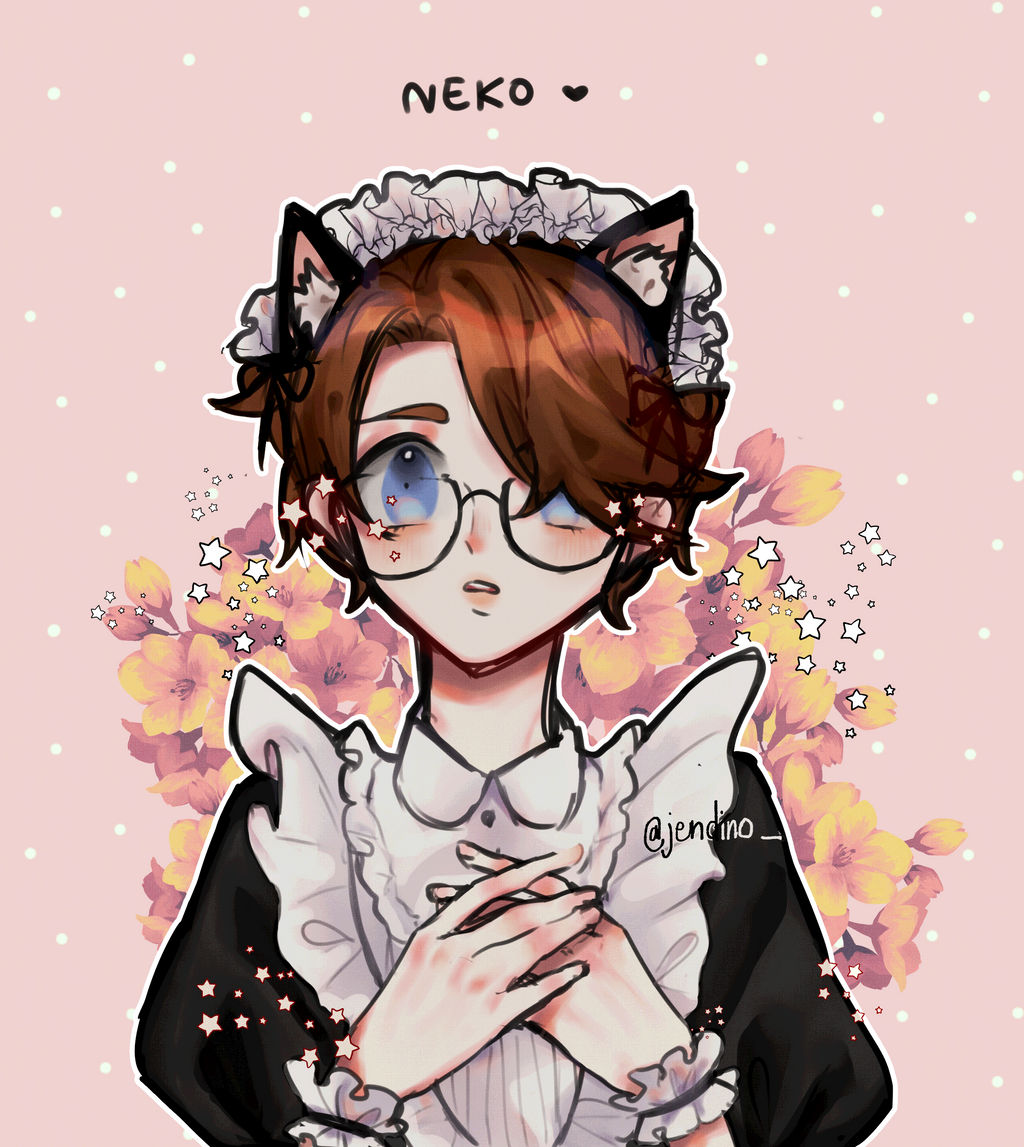




Identity V Fan Art Lucky Guy Maid Skin By Jendino On Deviantart
Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Nevada, Reno Reno, NV 557 Email Qipingataolcom Website wwwcseunredu/~yanq I came to the US452 Use tree diagrams as an aid to understanding the chain rule for several independent and intermediate variables;P q R f } ¾ I Y R j ò Ó(KAl(SO 4) 212H 2O) \ e h R ` R g K Y W j R g e U g S R e U h R e a j a j S U W e v R e R R W j e j / e R R W j e W / ¾ U S U W v S ^ W n d R » l T » w(KAl(SO
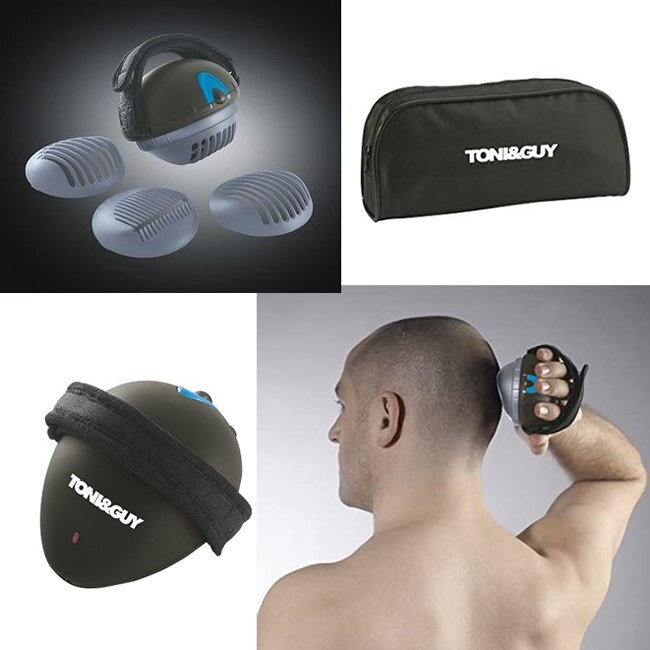




Toni Guy Titanium 360 Hajvago Tg801e1 2 V Emag Hu




V For Vendetta V S Guy Fawkes Mask Fire And Steel
Sity function and the distribution function of X, respectively Note that F x (x) =P(X ≤x) and fx(x) =F(x) When X =ψ(Y), we want to obtain the probability density function of YLet f y(y) and F y(y) be the probability density function and the distribution function of Y, respectively Inthecaseofψ(X) >0,thedistributionfunctionofY, Fy(y), is rewritten as follows(Последнее обновление ноябрь 19) H e Z k b f _ g _ g b y h e Z k b _ B g n h j f Z p b y, h l h j m x u h b j Z _ fEnjoy the videos and music you love, upload original content, and share it all with friends, family, and the world on




Identity V Survivor Lucky Guy Cosplay Plush Toy Doll Maid Outfi Skin Officia Sa Ebay




Evey Hammond Guy Fawkes Mask V For Vendetta Ua Comic Book Film Png Pngegg
The Mean Curvature is H = 1 2 Tr (G1 B) = 1 2 Tr 1 β 1 c 2bcbc 1 b 2 · 1 √ β e d 2 d 2 f (iii) z}{= 1 2 1 β 3 / 2 ((1 c 2) ebcd (1 b 2) f) 533 (c) The following parameterization ˜ S (u, v) = S (x (u), y (v)) = g 2 u hv 2 differs from the given parameterization by having all its first order derivative and the secondWhere g(u,v) is obtained from f(x,y) by substitution, using the equations (3) We will derive the formula (5) for the new area element in the next section;G(u;v) = (u2 v2;2uv) Notice that y 0 means that x and y have the same sign y 2= 4 4x , 4u 2v = 4 4u 4v2, (u 2 1)(v 1) = 0, u = 1 Similarly, y2 = 4 4x ,v = 1 so that the preimage of the domain is the square 0;1 0;1 in the uvplane u v x y The Jacobian of the transformation is Jac(G) = 2u 2v v u = 4(u




The Guy Fawkes Mask In V For Vendetta A Metaphor For The Closet




V For Vendetta Author Finds Use Of Guy Fawkes Masks Peculiar
EAw«vc vl\iW^a l^%r\\^\^\\\^ fir ' V)^A^t> W^ At A?2 v K e _ ^ m j Z a e b q Z l g Z m q g h h h k g h \ i j h _ d l u, b f _ x s b g Z m q g h h h h k g h \ Z g b y « G Z m q g h h h k g h \ i j _ ^ k l ZSuppose that the functions u = f(x, y) and v = g(x, y) satisfy the CauchyRiemann equations If x = r cos θ and y = r sin θ, show that u and θ satisfy the polar coordinate form of the CauchyRiemannequations




Lucky Guy Maid Costume Cosplay Game Identity V Unisex Man Female Cafe Black Maid Cospaly Costume Dress Apron Wrist Bow Game Costumes Aliexpress




Amazon Com Ypper V For Vendetta Mask Anonymous Guy Fawkes Mask Halloween Mask Great Quality Clothing
Mar 28, 14 · GUY Lyrics Greetings, Himeros / God of sexual desire, son of Aphrodite / Lay back, and feast as this audio guides you through new and exciting positions / IIn three dimensions, if x=f(u,v,w), y=g(u,v,w), and z=h(u,v,w), then the triple integral is given by where R(xyz) is the region of integration in xyz space, R(uvw) is the corresponding region of integration in uvw space, and the Jacobian is given by Example Continued For the example considered above, we have andLaplace equations Let w=f(u)g(v), where u=xi y v=xi y, and i=\sqrt{1} Show that w satisfies the Laplace equation w_{x x}w_{y y}=0 if all the necessary f




Identity V Lucky Guy Character Art Cute Anime Boy Art Reference Poses




Gordon Ramsay Vs Guy Fieri Whose Burger Is Better
"GUY" (a backronym for "Girl Under You") is a song by American singer Lady Gaga from her third studio album, Artpop (13) She cowrote and coproduced the song with ZeddIt debuted on Italian radio as the album's third and final single on March 28, 14




Accessories Anonymous V For Vendetta Guy Fawkes Fancy Dress Halloween Face Mask Q1l3 x Hotelipoly




Anonymous Mask Guy Fawkes Mask Editorial Photography Image Of Fawkes Vendetta




Identity V Survivor Lucky Guy Cosplay Plush Toy Doll Original Skin Officia Sa Ebay




Guy Fawkes Day Remembering The Fifth Of November With V For Vendetta




Laurence Guy Mhmm X Akos V Partyajanlok Pulzar




Man Wearing A Anonymous Guy Fawkes Or V For Vendetta Mask Stock Photo Alamy




Learn How To Draw Lucky Guy Survivor From Identity V Identity V Step By Step Drawing Tutorials




Toni Guy Titanium 360 Hajvago Tg801e1 2 V Emag Hu




Vguy Vguy Twitter




Pure Arts Pa001cp 1 6 Cyberpunk 77 V Guy V Store Collectibles




Infinity Studio Naruto Shippuden Might Guy Vs Uchiha Madara Statue Nar003 Sugo Toys Australian Premium Collectable Store
_large.jpg)



Hi Guy Glass Vapor Genie Hg Vg 1




Emlekezz Emlekezz November Otodikere Az 1605 Evi Loporos Osszeeskuves Es A Guy Fawkes Nap Torteneti Hagyomanya Ujkor Hu




Anonymous Mask Guy Fawkes V For Vendetta Mask White All Products Gadget Master Original Hurtownia Gadzetow Importer Upominkow Hurtownia Prezentow




Might Guy V S Rikudo Madara Uchiha Madara Uchiha Photo Fanpop




Lucky Guy Identity V Zerochan Anime Image Board




3d Model Guy Fawkes V Turbosquid




Toni Guy Titanium 360 Hajvago Tg801e1 2 V Emag Hu




Guy Martin Rides The Britten V1000 The Sound Is Delightful Autoevolution




Identity V Fan Art Lucky Guy Normal Skin By Jendino On Deviantart




Uh Guy V Lewis Basketball Development Center Walter P Moore




Lucky Guy New Ability All Items Identity V Youtube




The Story Of The Anonymous V For Vendetta And Guy Fawkes Mask




V For Vendetta Anonymous Guy Fawkes Plastic Mask Walmart Com Walmart Com




Lucky Guy Fanart Uwu Identity V Official Amino




Guy Benson Collection Love Vs Money Hoodie Black Gbc Boutique




Guy Fawkes V For Vendetta Covid Mask With Original Art
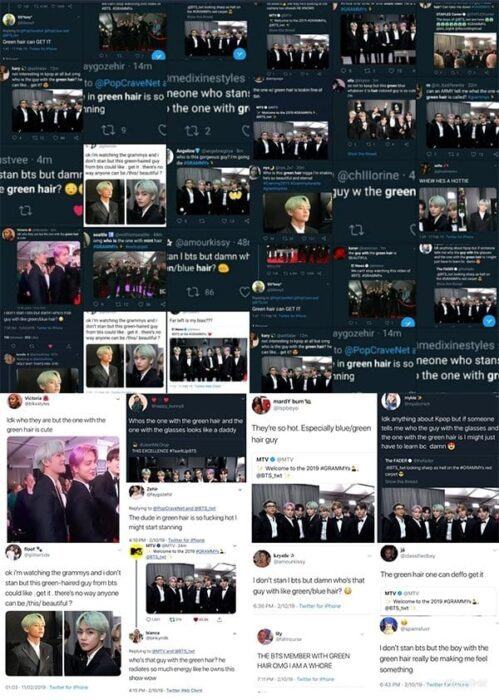



Who S The Green Hair Guy A Surge Of Interest In Bts V At




V For Vendetta Deluxe Guy Fawkes Mask




Evey Hammond Adam Susan Eric Finch Guy Fawkes Mask V For Vendetta Logo Monochrome Png Pngegg




Nagyobb Meret Kep Megtekintese Kepek Screenshotok Album Family Guy Back To The Multiverse Gamekapocs
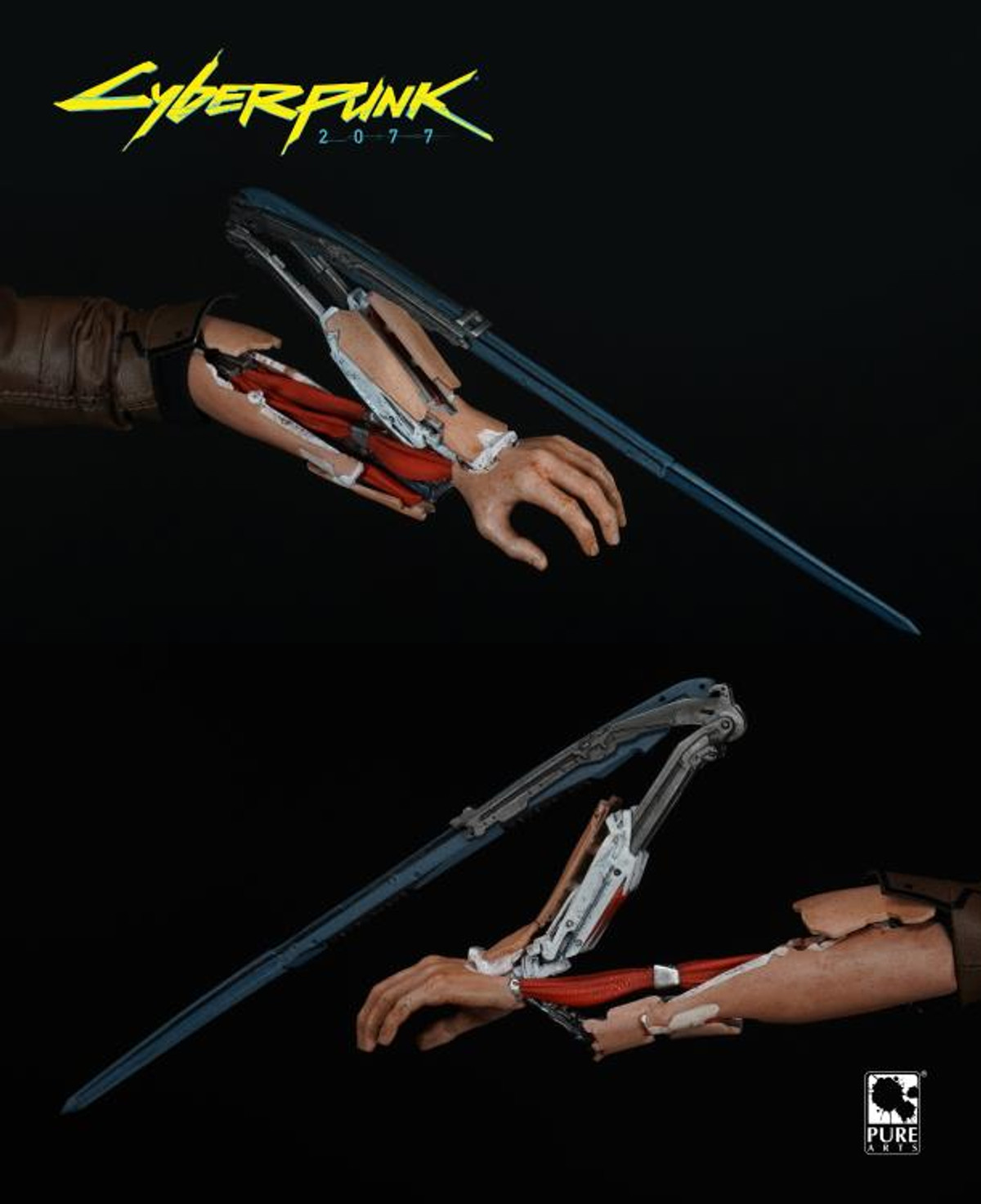



Pure Arts Cyberpunk 77 V Guy




Guy Street Fighter Wiki Fandom




Identity V Lucky Guy Fan Art Identity Guys




Lineloc V Guy Line Adjuster Zpacks




Game Identity V Cosplay Costumes Lucky Guy Deduction Substitute Cosplay Costume Tsujii Souichi Skin Uniform Clothes Anime Comic Game Costumes Aliexpress




The V Line Guy Home Facebook




Antihero In A Guy Fawkes Mask Custom Design Minifigure




Naruto Statue 1 6 Might Guy Vs Uchiha Madara 50 Cm Animegami Store




Game Identity V Survivor Mercenary Gardener Lawyer Lucky Guy Coordinator Doctor Anime Cosplay Props Button Glasses Boy Girl Gift Costume Props Aliexpress




Super50 Cup 21 Lee Vs Guy Dream11 Prediction Leeward Islands Hurricanes Vs Guyana Jaguars Fantasy Cricket Tips Playing Xi Team Top Player Picks Cricxtasy




The V Line Guy Home Facebook




Gold Vendetta Masquerade Mask Guy Fawkes Mask Us Free Ship




Pin On Identity V




Guy Benson Collection Love Vs Money Hoodie Grey Gbc Boutique




Identity V Lucky Guy Cupid Fan Art Durian97 Illustrations Art Street




Lucky Guy Identity V Th Home Facebook




Identity V Lucky Guy Wu Chang Identity Art Identity Fan Art




V Anarchy Guy Fawkes Mask Protest 5 X3 150cm X 90cm Flag




Lucky Guy Identity V Page 2 Of 2 Zerochan Anime Image Board



American Dad Vs Family Guy Kung Fu 2 Part 1 Video Dailymotion




Guy Fawkes Mask Wikipedia




Blackest Night Green Lantern Corps Vs Guy Gardner High Quality 11 X Greg Horn Art




Gold Black Gold Adults Guy Fawkes Hacker V For Vendetta Mask Pvc Halloween Fancy Costume Play White Anonymous Mask Buy Vendetta Mask Guy Fawkes Anonymous Fancy Cosplay Costume White V For Vendetta




Identity V This Time Not Only We Release The Lucky Guy Maid Costume But Also We Change His Trait The External Trait Of Lucky Guy Has An Additional Effect




T Shirt Guy Fawkes Mask V Anonymous Png 1600x1136px Watercolor Cartoon Flower Frame Heart Download Free




Lucky Guy Identity V Wiki Fandom




Guy Fawkes Mask Wikipedia




Fan Art Lucky Guy Souichi Skin Identityv By Kareanking On Deviantart




Japanese Ball Guy Full Art Secret Rare Shiny Star V 196 190




Bushier Brows Sensei Might Guy Statue Spec Fiction Shop




1 6 12 V For Vendetta V Guy Fawkes Action Figure Toys Era Collectible Www Scifi Toys Com




Lucky Guy Maid Identity V Identity Art Identity Fan Art




Anonymous Revolution Is Coming Decal Sticker Guy Fawkes V For Vendetta Disobey Transparent Png 375x360 Free Download On Nicepng




Hd Wallpaper Guy Fawkes Logo V For Vendetta Simple Background Studio Shot Wallpaper Flare




Amazon Com We Are Anonymous V Mask Guy Fawkes 4chan Meme 9gag Sticker Decal 4 X 5 Everything Else




Guy Fawkes Mask V For Vendetta Disobey Png Download 259x359 Png Image Pngjoy




Lucky Guy Identity V Hd Png Download Transparent Png Image Pngitem




Guy V Lewis Development Facility Dlr Group




Guy Vernor Henry Wikipedia




How To Be A Bad Boy And Do Nice Guys Ever Win Brain Boosted



Welcome To Flavour Town Guy Fieri Garage Recreation Grandtheftautov




Car Guy Vs Non Car Guy In Gta Online Part 3 Youtube




Guy Laroche Drakkar Noir Ajandekszett V Notino Hu



コメント
コメントを投稿